Low-speed operation of inverter-driven asynchronous motors presents a unique thermal challenge that can impact reliability and efficiency. Understanding the cooling requirements and selecting inverter-rated asynchronous motors is crucial for industrial users. With solutions such as auxiliary fans, enhanced ventilation, high-class insulation, and optimized design, asynchronous inverter motors can operate safely and efficiently under varying speed conditions. Consulting with experienced asynchronous motor manufacturers ensures that the motor selection and installation meet operational demands while providing long-term performance stability.
1. Why Cooling Becomes a Problem at Low Speed
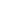
Standard asynchronous motors rely on fans mounted on the rotor shaft for cooling. These fans generate airflow proportional to rotor speed. When the motor runs at low frequency under an inverter:
Airflow decreases drastically, reducing heat dissipation.
Heat generated by electrical losses, such as copper and iron losses, accumulates inside the motor.
Reduced cooling can elevate winding temperature, increasing the risk of insulation degradation.
Industries such as textile manufacturing, conveyor systems, packaging lines, and printing equipment often operate motors at varying speeds.



2. Thermal Implications of Low-Speed Operation
Increased Thermal Resistance: At low speeds, heat transfer from the windings to the motor frame is less efficient, creating thermal resistance.
Localized Hot Spots: Uneven heating can result in hotspots in the stator or rotor, accelerating insulation aging.
Insulation Degradation: Persistent overheating weakens insulation, increasing the risk of partial discharge, insulation breakdown, and motor failure.
Reduced Efficiency: Excessive heat diminishes motor efficiency, as energy is lost in the form of heat rather than mechanical output.
Impact on Bearings and Lubrication: Elevated temperatures can also affect bearings, reducing lubrication effectiveness and increasing wear.
3. Design Strategies for Effective Cooling
Manufacturers of asynchronous inverter motors implement several strategies to ensure proper cooling even at low speeds:
Auxiliary or Independent Fans: Fans not directly connected to the rotor ensure continuous airflow regardless of motor speed.
Enhanced Ventilation: Redesigning motor housing with optimized airflow channels promotes natural or forced convection.
High Thermal-Class Insulation: Using Class H or Class F insulation withstands higher temperatures, prolonging motor lifespan.
Rotor and Stator Design Optimization: Modifying slot shapes and winding layouts improves heat dissipation efficiency.
Temperature Sensors and Thermal Protection: Embedding sensors allows monitoring and triggers inverter adjustments or shutdown when temperatures exceed safe thresholds.
Use of Heat-Conductive Materials: Incorporating materials with high thermal conductivity in motor construction helps spread heat more evenly.
These design enhancements ensure the motor can operate safely and reliably across a wide range of speeds and applications.
4. Practical Recommendations for Industrial Users
Industrial users should consider the following to mitigate low-speed cooling challenges:
Select Inverter-Rated Motors: Always choose asynchronous motors rated for inverter operation. Standard motors may not handle low-speed thermal stress.
Monitor Motor Temperature: Implement regular checks of winding and bearing temperatures to detect overheating early.
Optimize Inverter Settings: Adjust voltage, frequency, and acceleration/deceleration ramps to reduce heat generation.
Maintain Proper Ventilation: Ensure installation does not block airflow, and consider adding ducting or external fans if necessary.
Consult Experienced Manufacturers: Partnering with established asynchronous motor manufacturers such as Zhejiang Ligong Motor Co., Ltd. provides guidance on good motor selection, installation, and maintenance.
5. Benefits of Properly Designed Inverter Motors
Using asynchronous inverter motors designed for low-speed cooling challenges offers several operational advantages:
Stable Performance: Motors maintain safe operating temperatures, preventing unexpected shutdowns.
Extended Motor Lifespan: High-quality insulation and effective cooling reduce the risk of premature failure.
Improved Energy Efficiency: Maintaining proper temperature ensures the motor operates closer to its rated efficiency.
Reduced Maintenance Costs: Lower risk of overheating decreases the frequency of rewinding, bearing replacement, or other repairs.
Application Versatility: Suitable for diverse industries, including machinery, textiles, food processing, printing, construction, and metallurgical applications.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى